 08 March 2017
The most distant galaxy yet observed by ALMA gives insight into first stars
08 March 2017
The most distant galaxy yet observed by ALMA gives insight into first stars
... the Universe was only 600 million years old, and it is populated with an abundance of interstellar dust mainly composed of silicon, carbon and aluminium. The dust grains are as small as a millionth of a centimetre across and are formed by an earlier...
 02 August 2016
Astronomers detect large void in the centre of our Galaxy
02 August 2016
Astronomers detect large void in the centre of our Galaxy
... Milky Way instead. Nevertheless, finding Cepheids within the inner realm of our own galaxy is notoriously difficult, as interstellar dust blocks out a lot of the visible light, thus hiding stars from view. This problem can be overcome...
 January 2022
Revealing the magnetic universe
January 2022
Revealing the magnetic universe
... where enormous black holes reside. A portion of the Lupus I cloud complex. Color shows the emission by interstellar dust grains observed by Herschel Space Observatory. Streamlines show the associated magnetic fields based on Planck polarization data...
 29 August 2016
Dust is the key to producing complex organic molecules in space
29 August 2016
Dust is the key to producing complex organic molecules in space
...? Did they form in situ through gas phase reactions or were they produced via reactions on the surface of interstellar dust grains? Using the Green Bank Telescope, the IRAM 30m millimetre radio telescope and the Submillimeter...
 04 April 2016
Astronomers have for the first time found gas-phase ammonia in a protoplanetary disc
04 April 2016
Astronomers have for the first time found gas-phase ammonia in a protoplanetary disc
... with water OPR (ortho-to-para ratios) values – ratios used to determine the formation temperature of ice on cold interstellar dust – can be taken as evidence that the Cm model is a correct description for the distribution of H2O and NH3 in the...
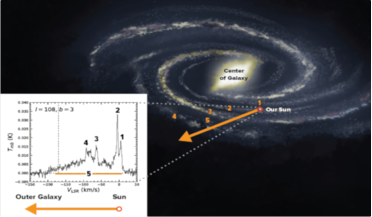 21 June 2021
Astronomers using GBT discover previously unknown huge galactic structure
21 June 2021
Astronomers using GBT discover previously unknown huge galactic structure
...known to produce a signal known as the 21-centimetre line in the ISM, and as it readily penetrates the clouds of interstellar dust particles that obstruct optical observations, it has allowed astronomers to map the galaxy’s spiral structure. But this...