 27 March 2019
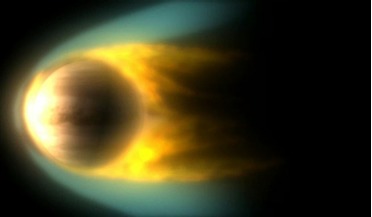
Storm-plagued exoplanet revealed in detail with GRAVITY
27 March 2019
Storm-plagued exoplanet revealed in detail with GRAVITY
... planets and planetary systems form. HR8799e is also completely inhospitable too; the exoplanet suffers from a powerful greenhouse effect – a bit like Venus – which heats the super giant to a scorching hot temperature of roughly 1000 °C. The...
 22 January 2020
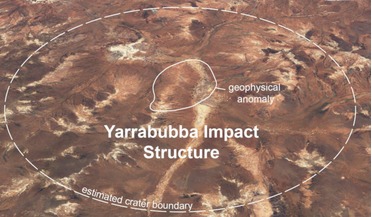
2.2 billion year old impact crater is confirmed as Earth's oldest
22 January 2020
2.2 billion year old impact crater is confirmed as Earth's oldest
... hit Earth when it was covered by an ice sheet between 2 to 5 kilometres thick, up to half a trillion tonnes of water vapour, a greenhouse gas, could have been released into the atmosphere from the melting ice within moments of the...
 05 June 2020
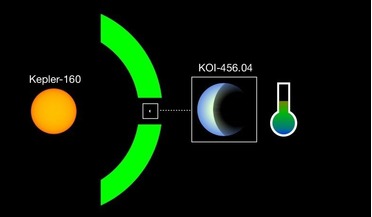
Exciting exoplanet find around sun-like star
05 June 2020
Exciting exoplanet find around sun-like star
....04 could be similar to those we have on Earth. “If KOI-456.04 has a mostly inert atmosphere with a mild Earth-like greenhouse effect, then its surface temperature would be +5 degrees Celsius on average, which is about ten degrees lower than...
 16 November 2020
Venus didn't lose water to space, new study says
16 November 2020
Venus didn't lose water to space, new study says
... in its structure, but above the surface the resemblance stops there. It’s thick atmosphere traps heat in a runaway greenhouse effect, making it the hottest planet in our solar system. The few glimpses that scientists have been...
 24 September 2021
New reactor could turn Mars' atmosphere into rocket fuel
24 September 2021
New reactor could turn Mars' atmosphere into rocket fuel
... to name just a few worrying effects. Wu and colleagues CO2 reactor could eventually help reduce this potent greenhouse gas. Currently under development, the team are experimenting with different catalysts such as graphene quantum dots...
 26 November 2021
A closer Moon could have helped the early habitability of our planet
26 November 2021
A closer Moon could have helped the early habitability of our planet
... evolve in these early stages have been suggested. These include an initially more massive Sun, an enhancement of greenhouse gases or a different cloud distribution which affected global albedo; albedo is the proportion of radiation that is reflected...