 October 2015
Down to Earth: how to deorbit satellites and save money
October 2015
Down to Earth: how to deorbit satellites and save money
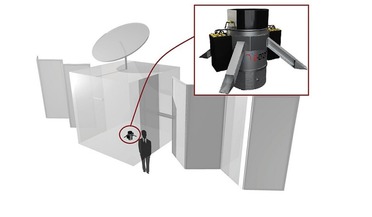
... or in some way make safe all forms of stored energy — both propulsive and electrical — in order to avoid possible explosions or break-ups in orbit after the end-of-mission. This passivation procedure is relatively complicated, and can result...
 October 2015
Green cosmonautics: an ideal to strive for
October 2015
Green cosmonautics: an ideal to strive for
... area size (overall capacity increase) Reliability - chances of having an accident during/after launch Toxicity and fire/explosion risks from rocket fuel, the level of pollution affecting the local environment, and the safety of areas...
 February 2016
Data Systems to Support Early Warning of Spaceborne Emergency Situations
February 2016
Data Systems to Support Early Warning of Spaceborne Emergency Situations
... across the Ural Mountain skies near the town of Chelyabinsk at just under 20 km/s, detonating in the atmosphere with an explosive yield approximately 25 times that of the bomb dropped on Hiroshima. Over 1500 people were injured, most due...
 March 2016
Gravitational waves provide new window on the universe
March 2016
Gravitational waves provide new window on the universe
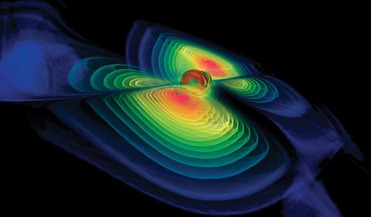
... 1: Comparison of Sun and Earth embedding diagram Black holes are formed when a massive star explodes in a cataclysmic explosion called a core-collapse supernova. The remnants of these types of dead star will form a black hole of a lower...
 August 2016
Academia’s role in space protection, space traffic management & orbital debris mitigation
August 2016
Academia’s role in space protection, space traffic management & orbital debris mitigation
... state-of-the possible, and help it become the state-of-practice in space operations. Sources of space debris include explosions of rocket bodies. Specifically, there are five key areas in which academia is uniquely positioned to become thought...
 October 2016
The dwarf galaxy problem
October 2016
The dwarf galaxy problem
... the idea that the hole in the ring-cloud could have been formed by a supernova (the death explosion of a massive star). This would have driven gas out of the local area and caused the hole...