 26 October 2020
Scientists detect molecular water and cold ‘water traps’ on the Moon
26 October 2020
Scientists detect molecular water and cold ‘water traps’ on the Moon
... water (H2O) or other hydroxyl (OH) compounds as both have chemical signatures at 3µm (micrometers) – the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum they were detected in – and it was difficult to discriminate between the two. Neither was it clear just...
 30 October 2020
It seems there might not be life on Venus after all, say two new studies
30 October 2020
It seems there might not be life on Venus after all, say two new studies
... Maxwell Telescope – the largest single-dish telescope that operates in the far-infrared to microwave wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. As ground-breaking as these results were, the team did not explicitly specify that microbes were behind...
 05 February 2021
Hydrazine might be present on Rhea, new study says
05 February 2021
Hydrazine might be present on Rhea, new study says
... a later study of this data revealed something intriguing; a portion of the light in the ultraviolet band of the electromagnetic spectrum, was being absorbed by a mysterious molecule. This absorption feature, that centred around 184 nanometers, was...
 15 February 2021
Possible planet found in habitable zone around Alpha Centauri
15 February 2021
Possible planet found in habitable zone around Alpha Centauri
... in infrared would not show blue skies and rocky continents for example, it is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum in which temperate Earth-like planets shine brightly in thermal emission. Infrared thermal imaging cameras on this planet...
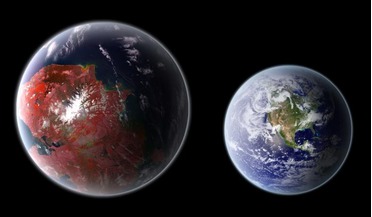 23 June 2021
Exoplanets with Earth-like biospheres may be rare
23 June 2021
Exoplanets with Earth-like biospheres may be rare
... by a planet from its host star. The energy they were specifically looking at comes from a region in the electromagnetic spectrum that corresponds more or less with the range of light visible to the human eye; a spectral range known...
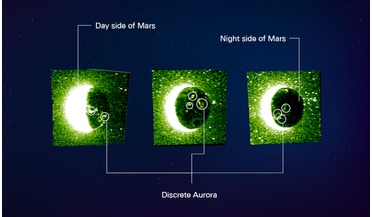 05 July 2021
Hope probe catches striking pictures of auroras at Mars
05 July 2021
Hope probe catches striking pictures of auroras at Mars
... its Emirates Mars Ultraviolet Spectrometer instrument to capture the auroras at a wavelength of 103.4 nanometres; a region of the electromagnetic spectrum that has shorter wavelengths than visible light, but longer than X-ray radiation. Although not...