 09 May 2016
Ancient silicate grains reveal histories of stardust in the Galaxy
09 May 2016
Ancient silicate grains reveal histories of stardust in the Galaxy
... research uncovered was that along with a wide range of chemical compositions, many of the silicate grains were amorphous in nature, meaning that they lacked a clearly defined shape – the opposite to a crystalline structure. However silicate crystals...
 February 2016
How to Build Planets
February 2016
How to Build Planets
... (Fe)-poor crystalline silicates, in particular forsterite and enstatite. Because the abundance of these species, relative to that of amorphous silicates, is far above the expected value for these grains in the interstellar medium, it is implied that...
 July 2016
Plasma Crystals - from space research to medicine on Earth and back to space again
July 2016
Plasma Crystals - from space research to medicine on Earth and back to space again
... and many laboratories entered the field. Figure 2 shows two pictures of ‘strongly coupled plasmas’ - on the left an ‘amorphous’ system, on the right a crystalline system surrounded by a fluid envelope. Figure 2: Two examples of three-dimensional...
 February 2019
Simulating lunar and martian regolith in the laboratory
February 2019
Simulating lunar and martian regolith in the laboratory
... material found on the surfaces of planetary bodies and is generally composed of rocks, mineral fragments, glass and amorphous particles, as well as various other geologically-derived materials. On Earth, regolith can be divided into various types...
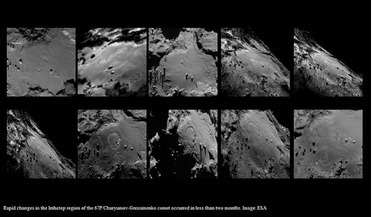 25 September 2015
67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko’s Imhotep region: conditions change rapidly on comet’s surface
25 September 2015
67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko’s Imhotep region: conditions change rapidly on comet’s surface
... specific process that’s wreaking all of this havoc in the Imhotep region. It could be anything from crystallisation of amorphous ice to destabilisation of particular molecules. What we do know is that such extreme, rapid changes were not originally...
 09 January 2016
Second Annual Buchalter Cosmology Prize awarded
09 January 2016
Second Annual Buchalter Cosmology Prize awarded
..., is a structure whose complexity is growing, with galaxy clusters, galaxies, and ultimately stars all emerging from an early amorphous soup of matter and energy. “Our conjecture is that our perception of time is the result of a law that determines...