 September 2017
Telescope targets enigmatic deep space mystery
September 2017
Telescope targets enigmatic deep space mystery
...exhibited a ‘dispersion’ sweep characteristic of all pulsars. Pulsars are ultra dense, rotating neutron star remnants of a supernova explosion in our Galaxy, which emit jets of radiation along their poles. As the pulsar spins, these jets of radiation...
 22 March 2016
Astronomers catch a supernova shock wave in visible light for the first time
22 March 2016
Astronomers catch a supernova shock wave in visible light for the first time
... bright star, before slowly fading from sight over several weeks or months. However the maximum intensity of a supernova explosion occurs after the shock wave and it is this period of peak brightness that is normally studied by astronomers. Therefore...
 25 July 2016
Supernova "Matryoshka" Discovered in Local Group
25 July 2016
Supernova "Matryoshka" Discovered in Local Group
.... This is the first time that researchers have found three concentric expanding supernova shells. Superbubbles are created by strong stellar winds and supernova explosions of individual stars, and are very varied in size and structure. The reason...
 03 April 2018
Astronomers unexpectedly find the most distant star ever discovered
03 April 2018
Astronomers unexpectedly find the most distant star ever discovered
... galaxy looking for something else. The space telescope had originally been set up to observe a gravitationally lensed supernova explosion nicknamed “Refsdal” in the galaxy cluster MACS J1149-2223, when it unexpectedly picked up the LS1 point source...
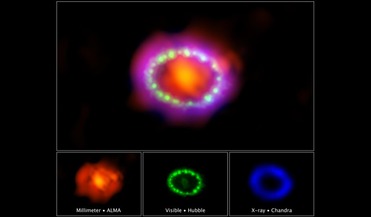 27 February 2017
Thirty years in the making - researchers show SN1987A in all of its glory
27 February 2017
Thirty years in the making - researchers show SN1987A in all of its glory
... movies and a three-dimensional model so that the public can ‘see’ a supernova explosion in as much detail as they possibly can. Just over three decades a go, supernova 1987A (SN 1987A), lit up the sky with the power of 100 million suns...
 March 2018
Exploring the extreme universe
March 2018
Exploring the extreme universe
... through nuclear fusion reactions, towards the ejection of stellar debris into interstellar space via winds and supernova explosions. Interstellar gas, enriched with newly produced nuclei, will eventually cool down to form new stars, hence...