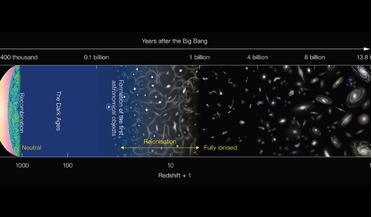
 29 January 2018
Astronomers discover a fossil of the Reionisation era
29 January 2018
Astronomers discover a fossil of the Reionisation era
... – burned for only a few million years before collapsing as supernovae. When the stars exploded, the energetic ultraviolet light emitted from ... more towards the idea that penetrating light from supernovae completely blew out the gas from the galaxy,...
 27 September 2019
TESS sees its first rare star-shredding event
27 September 2019
TESS sees its first rare star-shredding event
... years in a galaxy the size of our own Milky Way. Supernovae, by comparison, happen every 100 years or so. Fortunately, scientists ...with the ground-based All-Sky Automated Survey for Supernovae (ASAS-SN), we were able to trigger multiwavelength follow...
 November 2017
Radiation protection for space colonists and travellers
November 2017
Radiation protection for space colonists and travellers
... nuclei, iron or even uranium if they come from more energetic events such as supernovae and black holes. High-speed atomic particles produced by supernovae and other energetic deep-space events are referred to as galactic radiation and...
 June 2019
Does the speed of light change with time?
June 2019
Does the speed of light change with time?
...later on, when physicists measured the redshifts of distant supernovae, their redshifts appeared to increase non-linearly, as ...change over time. Measurements of the ‘constant’ from supernovae, those which appear to show acceleration, disagree with ...
 February 2022
Extremophiles as a blueprint for universal life
February 2022
Extremophiles as a blueprint for universal life
...Earth. Moreover, it is highly likely that the supernova blast that initially triggered the formation of our ...such as on massive stars or in the shock waves of supernova explosions. Deinococcus radiodurans protects itself from radiation in a different...
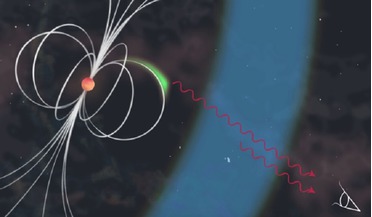 13 January 2016
High-energy theory models questioned as neutron star produces most energetic pulsed emission radiation ever detected
13 January 2016
High-energy theory models questioned as neutron star produces most energetic pulsed emission radiation ever detected
A neutron star in the centre of the supernova of 1054 A.D., known as the Crab pulsar... have formed by the gravitational collapse of a once massive star after a supernova explosion. This explosion was then responsible for creating the Crab nebula, a ...