 24 February 2020
First results from InSight reveal a seismically active Mars
24 February 2020
First results from InSight reveal a seismically active Mars
... a picture of what the uppermost layers of the Martian crust are alike. According to their paper, Mars is encased by a regolith layer just a few metres in depth, under which a much deeper crustal layer extends down to 8 and 11 kilometres...
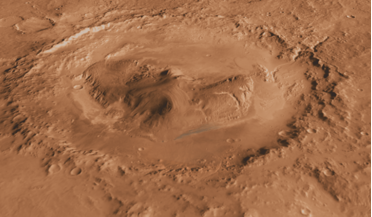 11 May 2020
Martian brines likely to be present, just not habitable says new study
11 May 2020
Martian brines likely to be present, just not habitable says new study
... be supported in nightly brines that are likely widespread through the shallow loose surface deposits known as Martian regolith. Now, a new study presented by a team of US astronomers and headed by Edgard Rivera-Valentín at the Lunar and Planetary...
 27 July 2020
Radiation-loving fungus could protect astronauts from cosmic rays
27 July 2020
Radiation-loving fungus could protect astronauts from cosmic rays
... hitting the Red Planet. However, if you combined the fungus with other in situ resources such as martian regolith, then a thinner layer of the black mould would suffice, say Shunk and colleagues. “Through the design...
 18 September 2020
NASA chiefs hint that Artemis will land at Apollo site, not lunar poles
18 September 2020
NASA chiefs hint that Artemis will land at Apollo site, not lunar poles
... shadowed craters on the Moon, scientists think that large quantities of water, either in ice or mixed with lunar regolith, could be available for human explorers to make use of. Water is a critical resource for long-term exploration, as it can...
 16 October 2020
SWRI tests "Clockwork Starfish" for sampling asteroids
16 October 2020
SWRI tests "Clockwork Starfish" for sampling asteroids
...in 2016. The initial experiment (BORE) was designed as a simple, no-moving-parts experiment to study the settling effects of regolith, as very little is known about the low-gravity geological processes on the surfaces of small bodies, explained Durda...
 23 November 2020
China's lunar sample return mission to launch tonight
23 November 2020
China's lunar sample return mission to launch tonight
... around two kilograms of samples by both scooping up surface material with a mechanical arm and by drilling through the regolith up to a depth of two metres. After sampling is complete, the ascender will transfer the collected materials to the...