 September 2017
Binary stars and their extraordinary lives
September 2017
Binary stars and their extraordinary lives
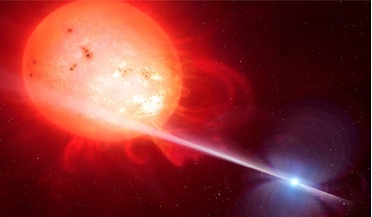
... 40 percent chance of being in a binary while among lower-mass red dwarfs, with masses one tenth of our Sun, the chance is below ...left pic) showing Mira A, a highly evolved red giant star, and Mira B, a white dwarf. Mira A is losing gas rapidly from ...
 September 2017
Science searches for cosmic company
September 2017
Science searches for cosmic company
... Dishes’ (LNSD) array designed to be highly effective for simultaneous surveys undertaken for SETI projects at centimetre wavelengths. Red dwarfs – stars that are both smaller and dimmer than the Sun – were traditionally of little interest to SETI...
 April 2019
Scanning the skies for exoplanets
April 2019
Scanning the skies for exoplanets
... than those the Kepler mission surveyed. HD 21749b’s host star (HD21749) on the other hand is classed as an M-dwarf or red dwarf. Red dwarfs range in mass from about 0.075 to about 0.50 solar masses and have a surface temperature of less than 3727...
 05 June 2020
Exciting exoplanet find around sun-like star
05 June 2020
Exciting exoplanet find around sun-like star
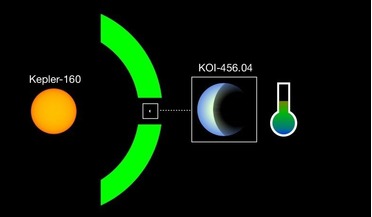
... present on their surface – the essential ingredient for life on Earth. Again though, these planets orbit red dwarf stars. Red dwarfs do have the advantage of having extremely long lifetimes, meaning that life trying to get a foothold on an exoplanet...
 14 November 2018
Super-Earth exoplanet found around closest single star to the Sun
14 November 2018
Super-Earth exoplanet found around closest single star to the Sun
... planet’s host star is Barnard’s star, a very low-mass red dwarf that shines only dimly in visible light, making it invisible to... as massive as Earth, but any similarities stop there. Although red dwarfs are by far the most common type of star in the ...
 07 January 2019
Two new firsts for exoplanets found by TESS
07 January 2019
Two new firsts for exoplanets found by TESS
... sequence stars that are intermediate in size between red M-type main sequence stars ("red dwarfs") and yellow G-type main-sequence stars (“yellow dwarfs”). As such K dwarfs often get called orange dwarfs. What is even more intriguing about the find...