 08 February 2017
Bridge between the Magellanic Clouds discovered
08 February 2017
Bridge between the Magellanic Clouds discovered
... measure the stars' properties. The astronomers are then able to locate various objects and events, including pulsars or explosions. The Cambridge team used Gaia data to study the Magellanic Clouds and locate RR Lyrae stars...
 23 March 2018
ESA selects ARIEL to look closely at exoplanets
23 March 2018
ESA selects ARIEL to look closely at exoplanets
... and evolve to produce the myriad of exoplanets we see today. Since the first confirmed detection of an exoplanet around a pulsar in 1991, thousands of exoplanets have been discovered and their diversity appears endless. All manner of exoworlds from...
 30 December 2019
Will Betelgeuse go supernova soon? Probably not say some astronomers
30 December 2019
Will Betelgeuse go supernova soon? Probably not say some astronomers
... likely it will leave behind a neutron star that will eventually turn into a fast spinning star called a pulsar. But still, the prospect of witnessing a supernova first hand and having telescopes ready to document the after...
 08 June 2020
New discovery provides important clues on mysterious cosmic bursts
08 June 2020
New discovery provides important clues on mysterious cosmic bursts
In 2007, while looking through archival pulsar survey data, two astronomers spotted something very unusual; fleeting bursts of radio wave emission caused by some ...
 26 June 2020
Giant ‘Exotica’ catalogue boosts search for alien life
26 June 2020
Giant ‘Exotica’ catalogue boosts search for alien life
... planet, stars with unusually high or low metal content, the most distant quasar and fastest-spinning pulsar, and the densest galaxy. 3) Anomalies: enigmatic targets whose behaviour is currently not satisfactorily explained. For instance...
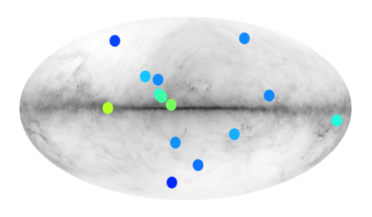 30 April 2021
Scientists identify 14 stars that could be made of antimatter
30 April 2021
Scientists identify 14 stars that could be made of antimatter
..., that these objects are not antistars, and instead are other types of gamma-ray emitters, such as pulsars or black holes, but further investigation will needed to rule this out. Keen to know just how many...