 29 July 2020
Puzzling new gas signatures found on Mars
29 July 2020
Puzzling new gas signatures found on Mars
... rover, but there is no direct disagreement between missions as the TGO data cannot account for large plumes of methane, only smaller amounts. “In fact, we’re actively working on coordinating measurements with other missions,” clarifies Kevin...
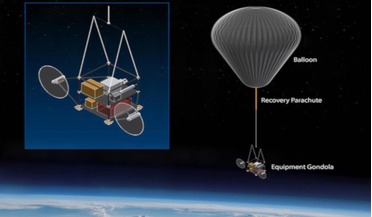 18 December 2020
Experiment to dim sunlight with chalk dust under review
18 December 2020
Experiment to dim sunlight with chalk dust under review
... carbonate into the stratosphere and will use the SCoPEx balloon to double back to observe the resulting plume. Injecting aerosols into the stratosphere to combat a warming climate does not come without risks, naturally. Scientists...
 05 February 2021
Hydrazine might be present on Rhea, new study says
05 February 2021
Hydrazine might be present on Rhea, new study says
... or exogenic delivery by micro-meteoroids and/or asteroids that contain chlorine. Chlorine-based salts have been detected in plumes of Enceladus, another of Saturn’s icy moons, a finding which led to the suggestion that the 500 kilometre-wide...
 26 March 2021
Enceladus could have ocean currents like those on Earth, new study says
26 March 2021
Enceladus could have ocean currents like those on Earth, new study says
... from Enceladus’ ocean at 400 metres per second (800 miles per hour). The material, which forms a plume that extends hundreds of kilometres into space, was a mixture of water and simple organic chemicals and pointed...
 13 April 2019
Enceladus and the Icy Moons of Saturn
13 April 2019
Enceladus and the Icy Moons of Saturn
... four main sections: the first on the geophysics, geology and geochemistry of Enceladus, the second on its famous plumes, the third on the other icy moons and the fourth on astrobiology and possible exploration of Enceladus. Why...
 13 December 2019
NASA selects Nightingale site for asteroid sample collection
13 December 2019
NASA selects Nightingale site for asteroid sample collection
...” from the site if its predicted position is too close to a hazardous area. During this maneuver, the exhaust plumes from the spacecraft’s thrusters could potentially disturb the surface of the site, due to the asteroid’s microgravity...