 March 2016
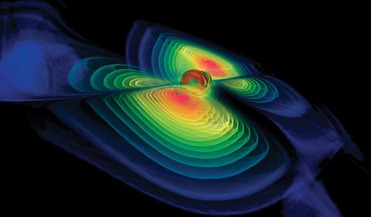
Gravitational waves provide new window on the universe
March 2016
Gravitational waves provide new window on the universe
...combined luminosity of every star and galaxy in the observable universe. Without the improved sensitivity of LIGO made in ... neutron with a black hole. With it, we might be able to observe gamma ray light emitted from a short gamma ray burst. If so, ...
 October 2020
Learning from alternative universes
October 2020
Learning from alternative universes
... by a factor of 1078. This period is called ‘Inflation’ and it explicitly explains why the observable universe appears uniform at large scales. We see the ‘afterglow’ of the Big Bang today in the form of Cosmic Microwave ...
 06 March 2020
Life in the Universe could be common, but not near us says study
06 March 2020
Life in the Universe could be common, but not near us says study
... space we consider to be the observable Universe. How big is the observable Universe. In one short answer, Big. “However, there is more to the universe than the observable," explains Totani. The observable Universe contains about 10 sextillion (1022...
 February 2022
Revolution and responsibility: the challenges of space
February 2022
Revolution and responsibility: the challenges of space
... drunk on the spectacle of the vaulted, we can be lulled by the figures quoted by astronomers who tell us that the observable universe has between 100 and 200 billion galaxies, each of them encompassing several hundred billion stars. This...
 22 May 2017
Researchers create largest-ever 3D map of the Universe
22 May 2017
Researchers create largest-ever 3D map of the Universe
...right hand edge of the map is the limit of the observable universe, from which we see the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) ...empty space in between the quasars and the edge of the observable universe are from the “dark ages”, prior to the formation of...
 16 May 2018
Astronomers find stars forming just 250 million years after Big Bang
16 May 2018
Astronomers find stars forming just 250 million years after Big Bang
... of the distant oxygen in the ALMA data,” says Hashimoto. “This detection pushes back the frontiers of the observable Universe.” Along with the ancient oxygen signal, the VLT also picked up a weaker signal of hydrogen emission which...