 February 2021
Space archaeology - preserving our orbital heritage
February 2021
Space archaeology - preserving our orbital heritage
... debris. For LEO, current guidance is that an asset should be safely de-orbited in a controlled fashion to burn up on re-entry. For satellites in geostationary orbit (GEO), the guidance is to place end-of-life hardware in a much higher ‘graveyard...
 29 June 2018
mu Space issues proposal request to build a satellite covering Asia-Pacific
29 June 2018
mu Space issues proposal request to build a satellite covering Asia-Pacific
...’s satellite with coverage spanning across Asia-Pacific. The high throughput satellite will be on a geostationary orbit (GEO) location at 50.5-degree East, an orbital slot secured on a recent agreement between mu Space and SES, the world’s leading...
 August 2017
Big science from small spacecraft
August 2017
Big science from small spacecraft
... radio telescopes on Earth because they are blocked by our ionosphere. If we could position a radio telescope up at geostationary orbit (GEO) or higher, well above the ionosphere, we could observe and characterise these short-lived phenomena, a long...
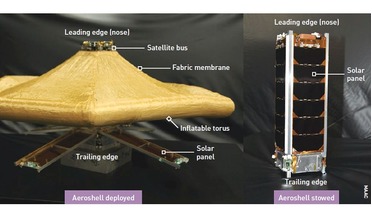 February 2020
Aeroshells – from LEO to Mars
February 2020
Aeroshells – from LEO to Mars
...deployment mechanism. Debris mitigation LEO is one of the most commercially valuable regions of outer space (second only to geostationary orbit, GEO), and is situated between altitudes of about 150 km and 2000 km. The key letter in the acronym is the...
 01 June 2021
Space junk collision highlights need for intervention
01 June 2021
Space junk collision highlights need for intervention
...larger than 5-10 cm in low Earth orbit (LEO) and 30 cm to 1 m in geostationary orbit (GEO) - as well as several thousands to millions of non-trackable debris particles in orbit around the Earth. “These in-orbit collisions and explosions highlight the...
 May 2019
Active debris removal faces legal minefield
May 2019
Active debris removal faces legal minefield
...measures to remove objects from low Earth orbit (LEO) and geostationary orbit (GEO) after the end of their missions... could apply to tacit consent in the context of these in-orbit operations. ESA is planning the world’s first ever active debris...