 29 November 2017
Deepest spectroscopic survey completed of the Hubble Ultra Deep Field
29 November 2017
Deepest spectroscopic survey completed of the Hubble Ultra Deep Field
... Telescope. And since then, 13 instruments on eight telescopes have observed the field covering nearly the complete electromagnetic spectrum from X-ray to radio wavelengths. Despite the years of research already conducted into the HUDF, with the...
 21 June 2017
LISA gets green light from ESA
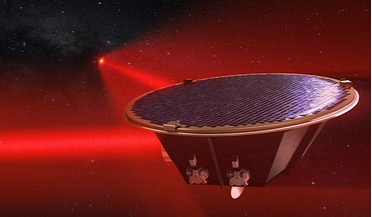
21 June 2017
LISA gets green light from ESA
... for waves at a higher frequency than what LISA will detect. By detecting gravitational waves within a broader spectrum of the electromagnetic spectrum, it could help scientists to understand the Universe in a whole new way, and could give insights...
 04 May 2020
Exoplanets with hydrogen-rich atmospheres could harbour life
04 May 2020
Exoplanets with hydrogen-rich atmospheres could harbour life
...boon for the study of exoplanetary atmospheres, as it operates at infrared (IR) wavelengths; the region of the electromagnetic spectrum that astronomers use to identify molecules, especially planetary atmospheric ones such as methane, carbon monoxide...
 15 June 2020
Green dayglow detected at Mars for the first time
15 June 2020
Green dayglow detected at Mars for the first time
...it emits light at wavelengthsaround 558 nanometers (nm), which corresponds to green light in the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Whilst it might appear everywhere in our atmosphere as green-light emission, so far, scientists have yet...
 16 June 2021
Astronomers discover the largest rotating objects in the Universe
16 June 2021
Astronomers discover the largest rotating objects in the Universe
... they move into the red end of the electromagnetic spectrum - they become redshifted. Lightwaves from an approaching...to shorten slightly and so move to the blue end of the spectrum, or become blueshifted - a phenomena known as Doppler shifting. Edwin...
 August 2016
High-resolution Earth observation data is changing the character of war
August 2016
High-resolution Earth observation data is changing the character of war
... the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 which collects information in 11 narrow bands of wavelengths on the electromagnetic spectrum. False-colour imagery is used to provide additional scientific insights - the near infrared (band 5) in this...