 June 2019
Does the speed of light change with time?
June 2019
Does the speed of light change with time?
... the speed of light. According to this equation, when t was small, c was enormous and the universe expanded in a Big Bang. As t increased expansion slowed due to G (gravity) and M (mass). The equation predicts that c is still slowing at a very small...
 02 December 2019
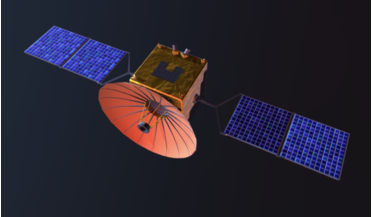
Chang'e 4 relay satellite now a radio telescope
02 December 2019
Chang'e 4 relay satellite now a radio telescope
...300 million years to one billion years after the Big Bang poses many challenges for astronomers as these ancient ...sensitive to signals from around 800 million years after the Big Bang with these shorter antennas, though once unfolded to their full...
 13 July 2018
Neutrino discovery helps resolve a century-old riddle
13 July 2018
Neutrino discovery helps resolve a century-old riddle
... created 10-4 seconds after the Big Bang. At a mere one second after the big bang, the Universe became transparent to... normal matter won the battle with antimatter so early after the Big Bang. This is to do with how the antineutrino in less inclined...
 26 July 2016
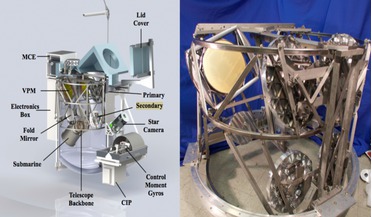
Will PIPER be successful in confirming Inflation Theory?
26 July 2016
Will PIPER be successful in confirming Inflation Theory?
...in the inflationary epoch that occurred just after the Big Bang. Cosmological inflation is the current leading theory for ...the universe. One such characteristic is the afterglow of the Big Bang known as the cosmic microwave background (CMB). The CMB ...
 18 November 2020
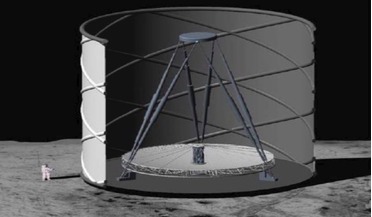
Astronomers want to revive idea for ‘Ultimately Large Telescope’ on the Moon
18 November 2020
Astronomers want to revive idea for ‘Ultimately Large Telescope’ on the Moon
... first stars marks a crucial transition in the history of the universe, when the primordial conditions set by the Big Bang gave way to an ever-increasing cosmic complexity, eventually bringing life to planets, life, and intelligent beings like...
 09 October 2019
This year's Physics Nobel Prize winners
09 October 2019
This year's Physics Nobel Prize winners
...basis of our contemporary ideas about the universe. The Big Bang model describes the universe from its very first moments, ...our understanding of how the universe evolved after the Big Bang, Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz explored our cosmic ...