 14 December 2016
Astronomers find a ring of new stars around the LMC
14 December 2016
Astronomers find a ring of new stars around the LMC
... the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of the closest neighbours to the Milky Way, is not yet finished with making stars. Not only that, but the stars are being formed in an unlikely part of the galaxy. The Large and Small Magellanic Clouds...
 08 February 2017
Bridge between the Magellanic Clouds discovered
08 February 2017
Bridge between the Magellanic Clouds discovered
... dwarf galaxies. Gaia has greatly simplified studying the Magellanic Clouds, as it is able to cover the large area over which they spread. The astronomers found that the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) has a low-luminosity halo that stretches as far...
 October 2016
The dwarf galaxy problem
October 2016
The dwarf galaxy problem
... Another possibility is that the ring-cloud is an extension of the Magellanic stream. This is a hydrogen stream that crosses the sky, originating at the Magellanic clouds (the small and large Magellanic clouds are actually two dwarf galaxies orbiting...
 26 September 2016
A potentially disrupting satellite system around the LMC has been observed for the first time by astronomers
26 September 2016
A potentially disrupting satellite system around the LMC has been observed for the first time by astronomers
The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) is a satellite dwarf galaxy of the ...the Observatoire astronomique de Strasbourg, France, found within the Survey of the Magellanic Stellar History (SMASH), a very faint stellar system approximately 16 kilo parsecs...
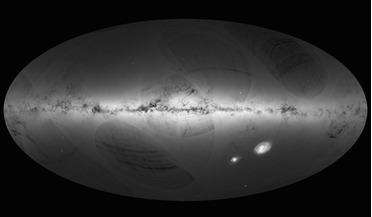 14 September 2016
Gaia's first map hints at big things to come
14 September 2016
Gaia's first map hints at big things to come
... to how Gaia will revolutionise all areas of astronomy, “this is only the beginning: we measured the distance to the Large Magellanic Cloud to test the quality of the data, and we got a sneak preview of the dramatic improvements that Gaia will...
 20 September 2018
TESS finds its first exoplanet – a super-Earth 60 light years away
20 September 2018
TESS finds its first exoplanet – a super-Earth 60 light years away
... has already come to fruition with the first round of data collected by this auspicious mission. A snapshot of the Large Magellanic Cloud (right) and the bright star R Doradus taken by TESS in its “first light” science image on 7 August, 2018...