Although the mission's cost has increased by a hefty $150 million, NASA had approved and completed a review of Key Decision Point B (KDP-B), the Asteroid Redirect Mission's robotic segment. As a result of the review, the mission cost has been increased and the robotic mission launch date has been postponed by a year, with the mission currently scheduled for 2021. Total mission cost estimate, set at $1.4 billion, does not include launch or operations costs.
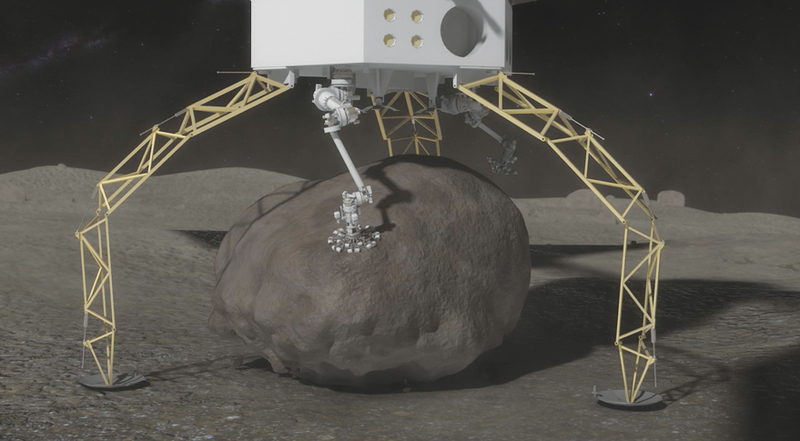
Asteroid Capture Microspine grippers on the end of the robotics arms are used to grasp and secure the boulder. The microspines use thousands of small spines to dig into the boulder and create a strong grip. An integrated drill will be used to provide final anchoring of the boulder to the capture mechanism. Credit: NASA artist’s concept
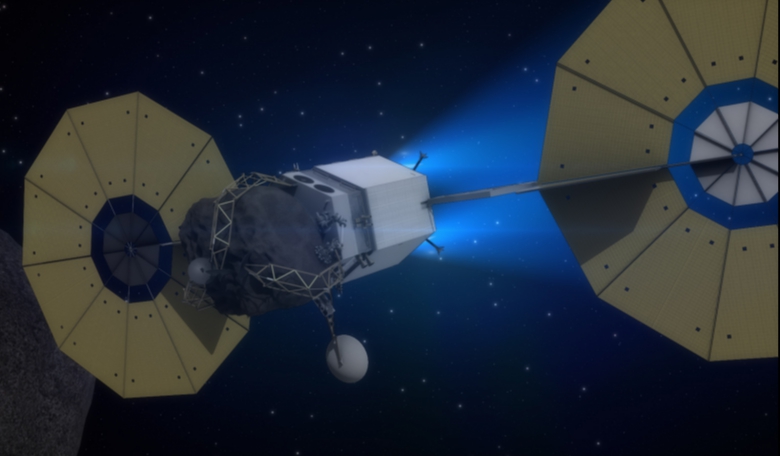
The Asteroid Redirect Mission is expected to send a robotic spacecraft to an asteroid in near-earth space. The spacecraft will retrieve a boulder of a few meters in diameter from the asteroid and bring it to cislunar space. An manned Orion mission, planned for 2026, will then visit the boulder for research purposes. The mission will also help gain invaluable experience for future manned Mars missions.
According to Michele Gates, ARM program manager at NASA, “With KDP-B under our belt, ARM can now move forward to define partnerships and opportunities for long-term engagement.” NASA will be seeking partnerships for hosted payloads to fly with the ARM robotic spacecraft, and looking for scientists to join the mission's “investigation team”. The release of these two solicitations has been delayed along with the mission, as they were originally planned for release in early August and have now been moved to September.